Biology Careers
GENERAL SKILLS
Research
Biologists experiment using techniques such as microscopy, genetic analysis, field observation, etc, to obtain data from living organisms and perform abiotic analysis.
Classification of Organisms
Biologists can classify organisms based on their physical characteristics, genetics, behavior, and other various factors. Relationships between various organisms can be made based on this data, and this can be applied to other biological fields like disease control.
Teaching
Biologists can train future biologists in every field to ensure that the trainees have the skills necessary to carry on their jobs proficiently. Biologists, from time to time, may also be called to companies, administrations, and schools to give lectures on various topics and teach students and parents.
Studying Genetics
Biologists may have to research the genetic codes of organisms in order to control and manipulate those traits through genetic engineering or gene editing. Techniques such as PCR and gel electrophoresis may be used to analyze genetic material.
Population analysis
Biologists may track populations of organisms in specific environments over a specific period of time by using remote sensing or population surveys. These biologists can also use this information and data to manage invasive species, protect endangered species, or restore habitats and increase biodiversity.
Disease analysis
Biologists can analyze the spread of disease and the causes for the spread of those diseases, and they may propose solutions to certain causes and create preventive measures.
Additional Information
Average Salary: $31K
Job Market: Approximately 135,000 biologists in the US.
Average Job Market Growth Per Decade: 4.7%
Average Education Level: Bachelor’s Degree
Molecular Biologist
Molecular Biologists are research heavy, particularly spending most of their time either collecting samples or performing experiments in the lab.
-
A bachelor’s degree in a field related to molecular biology is the minimum. However, many employers require at least a masters degree.
-
A typical workday as a molecular biologist does not have a set structure. A day could be spent doing tasks from picking up worms at lakes to growing cells in the lab.
Molecular Biologist Lab Equipment & Techniques
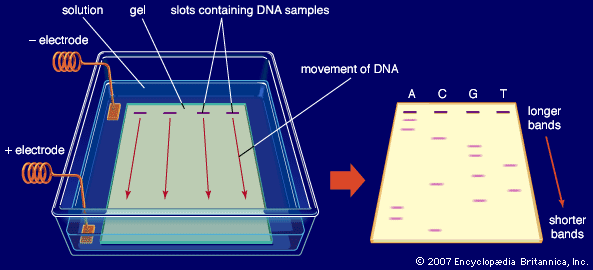
Gel electrophoresis and PCR technique
PCR: Utilizes rapid heat and centrifuge techniques with restriction enzymes and genetic material to quickly duplicate and multiply DNA thousands of times.
This allows for enough genetic material to be analyzed.
After, scientists utilize gel electrophoresis which sends a current through gel, and putting genetic material separates them based on their size.
This allows to see if certain traits are present
Botanists
Botanists study the relationship between organisms and the environment. One of the main focuses is to grow plants better/more efficiently.
-
Most botanists have a bachelor’s degree in botany and plant professions.
Example Botanist Task
An example of a botanist’s task: investigate gene expression in a small plant named Arabidopsis Thaliana, and create a number of crops that can survive harsh and non-constant environmental circumstances.
The scientist can set up seed samples and utilizes In Situ hybridization. What this experiment does is it locates the genetic material (RNA in this case) by adding probes and analyzing the entire thing under a microscope.
This scientist can also utilize single-nuclei RNA sequencing, which collects data on gene expression of RNA: essentially, it checks whether any piece of RNA is expressed as a protein or not.
The scientist finally can carry out In Situ hybridization, and also utilizes single-nuclei RNA sequencing to discover new peptide sequences that create unique proteins. Through data analysis of the flower’s offspring, the scientist can formulate a new hypothesis that the new proteins found had impact in seed development not related to fertilization.
Neurobiologist
Cognitive neuroscientists analyze the nervous system the most and its interactions with muscles, environment, electrical activity, etc. Most neuroscientists are scientists who aim to research how to improve conditions.
Neurobiologist Lab Equipment & Techniques
PET
Scientists inject a small amount of radioactive material, which then they utilize a PET scan machine to create a 3D image where the machine picks up on the radiation, mapping a picture of where the radioactive material goes. If put in the brain, the material usually goes to the areas where the brain is used, so it maps brain structure and usage of each structure.
CT
A type of x-ray where structural components of the brain are mapped out. Does not really analyze usage of brain parts, rather focuses on structural components.
MRI
Utilizes magnetic resonance in order to map out structural components of the brain. Furthermore, an fMRI can be used to map out brain activity.